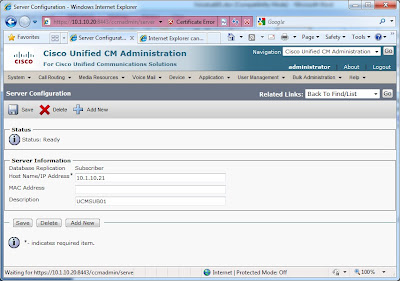
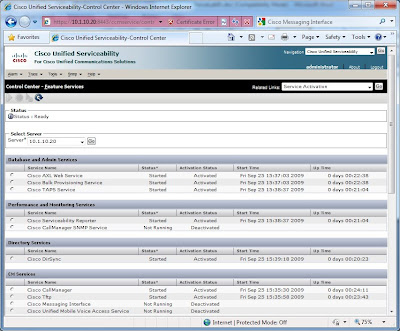
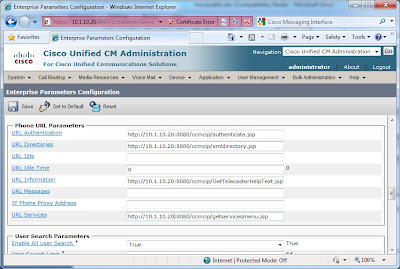
Rather than dissect each sub-task individually, I will review each device, and then circle back around on verifying connectivity. One thing to keep in mind with the CCIE LAB, you needn’t necessarily configure everything in the order presented in the lab guide.
1. Below is the configuration for the frame relay switch. Also note, I’ve configured this router to synchronize with an NTP server on the Internet. This router will then act as the NTP server for the lab devices.
ISP#
!
clock timezone EST -5
clock summer-time EDT recurring
!
frame-relay switching
!
!
interface Serial0/0/0
description frame-relay link to London
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
no fair-queue
clock rate 128000
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
frame-relay intf-type dce
frame-relay route 301 interface Serial0/0/1 103
!
interface Serial0/0/1
description frame-relay to New York
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
clock rate 128000
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
frame-relay intf-type dce
frame-relay route 102 interface Serial0/1/0 201
frame-relay route 103 interface Serial0/0/0 301
!
interface Serial0/1/0
description frame-relay link to Los Angeles
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
clock rate 128000
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
frame-relay intf-type dce
frame-relay route 201 interface Serial0/0/1 102
!
ntp source FastEthernet0/0
ntp update-calendar
ntp server 198.82.1.201
2. Next, we’ll take a look at the New York router. First, the basic configuration parameters for the IP addressing, including the WAN (frame relay) and LANs/VLANs.
newyork#
!
interface FastEthernet0/0.1
description link to Internet
encapsulation dot1Q 1 native
ip address 10.1.1.101 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/0.10
description New York Server VLAN
encapsulation dot1Q 10
ip address 10.1.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/0.11
description New York Data VLAN
encapsulation dot1Q 11
ip address 10.1.11.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/0.12
description New York Voice VLAN
encapsulation dot1Q 12
ip address 10.1.12.1 255.255.255.0
!
!
interface Serial0/2/0
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
!
interface Serial0/2/0.102 point-to-point
description frame relay link to Los Angeles
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252
ip ospf network point-to-point
frame-relay interface-dlci 102
!
interface Serial0/2/0.103 point-to-point
description frame relay link to London
ip address 172.16.1.5 255.255.255.252
ip ospf network point-to-point
frame-relay interface-dlci 103
!
Next, the routing, including a default route to the Internet:
!
router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
log-adjacency-changes
network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
network 10.1.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
network 10.1.11.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
network 10.1.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.3
Finally, some of the key “IP services” configuration in the router, including the DHCP scopes:
!
service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezone year
service timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezone year
!
clock timezone EST -5
clock summer-time EDT recurring
!
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.11.1 10.1.11.15
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.12.1 10.1.12.15
!
ip dhcp pool newyork-data
network 10.1.11.0 255.255.255.0
update dns both
default-router 10.1.11.1
domain-name ballplayersllc.com
dns-server 10.1.10.11 4.2.2.1
!
ip dhcp pool newyork-voice
network 10.1.12.0 255.255.255.0
update dns both
default-router 10.1.12.1
domain-name ballplayersllc.com
option 150 ip 10.1.10.20
dns-server 10.1.10.11 4.2.2.1
!
!
ip domain name ballplayersllc.com
!
ntp source FastEthernet0/0.1
ntp update-calendar
ntp server 10.1.1.43. Below is are the pertinent pieces of the configuration for the 3750 switch for the New York LAN/VLANs.
s1-newyork#
!
interface FastEthernet1/0/2
description to NewYork
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,10-12
switchport mode trunk
spanning-tree portfast trunk
!
!
interface FastEthernet1/0/8
description newyork phones
switchport access vlan 11
switchport voice vlan 12
spanning-tree portfast
!
interface FastEthernet1/0/9
description newyork phones
switchport access vlan 11
switchport voice vlan 12
spanning-tree portfast
!
interface FastEthernet1/0/10
description newyork phones
switchport access vlan 11
switchport voice vlan 12
spanning-tree portfast
!
!
interface Vlan1
ip address 10.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan10
description newyork-management
ip address 10.1.10.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan11
description newyork-data
ip address 10.1.11.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan12
description newyork-voice
ip address 10.1.12.2 255.255.255.0
!
4. Next stop is Los Angeles. The configuration here is very similar to New York. Note, this router uses a 4-port Ethernet Switch HWIC module.
losangeles#sh start
!
clock timezone PST -8
clock summer-time PST recurring
!
!
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.21.1 10.1.21.15
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.22.1 10.1.22.15
!
ip dhcp pool losangeles-data
network 10.1.21.0 255.255.255.0
update dns both
default-router 10.1.21.1
dns-server 10.1.10.11 4.2.2.1
domain-name ballplayersllc.com
!
ip dhcp pool losangeles-voice
network 10.1.22.0 255.255.255.0
update dns both
default-router 10.1.22.1
dns-server 10.1.10.11 4.2.2.1
domain-name ballplayersllc.com
option 150 ip 10.1.10.20
!
!
ip domain name ballplayersllc.com
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
description link to Internet
ip address 10.1.1.102 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/3/0
description losangeles ip phones
switchport access vlan 21
switchport voice vlan 22
!
interface FastEthernet0/3/1
description losangeles ip phones
switchport access vlan 21
switchport voice vlan 22
!
interface FastEthernet0/3/2
description losangeles ip phones
switchport access vlan 21
switchport voice vlan 22
!
interface FastEthernet0/3/3
description losangeles ip phones
switchport access vlan 21
switchport voice vlan 22
!
interface Serial0/2/0
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
!
interface Serial0/2/0.201 point-to-point
description frame relay to New York
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.252
ip ospf network point-to-point
snmp trap link-status
frame-relay interface-dlci 201
!
!
interface Vlan20
description Los Angeles Server VLAN
ip address 10.1.20.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan21
description Los Angeles Data VLAN
ip address 10.1.21.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan22
description Los Angeles Voice VLAN
ip address 10.1.22.1 255.255.255.0
!
router ospf 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
log-adjacency-changes
network 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
network 10.1.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
network 10.1.21.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
network 10.1.22.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.3
!
ntp source FastEthernet0/0
ntp update-calendar
ntp server 10.1.1.45. London’s configuration is very similar to the other locations, with a few exceptions. First, the option 150 command for the voice DHCP scope points to the router, since this is will be a CUCME location. Also, London’s router has an NME-16ES-1G-P, which from the perspective of the router, looks like an independent switch.
london#sh start
!
clock timezone GMT 0
clock summer-time BST recurring
!
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.31.1 10.1.31.15
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.32.1 10.1.32.15
!
ip dhcp pool london-data
network 10.1.31.0 255.255.255.0
update dns both
default-router 10.1.31.1
dns-server 10.1.10.11 4.2.2.1
domain-name ballplayersllc.com
!
ip dhcp pool london-voice
network 10.1.32.0 255.255.255.0
update dns both
default-router 10.1.32.1
domain-name ballplayersllc.com
dns-server 10.1.10.11 4.2.2.1
option 150 ip 10.1.30.1
!
!
ip domain name ballplayersllc.com
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
description link to Internet
ip address 10.1.1.103 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!
!
interface Serial0/2/0
no ip address
encapsulation frame-relay
frame-relay lmi-type cisco
!
interface Serial0/2/0.301 point-to-point
description frame relay to New York
ip address 172.16.1.6 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-point
snmp trap link-status
frame-relay interface-dlci 301
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0
no ip address
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0.30
description London Server VLAN
encapsulation dot1Q 30 native
ip address 10.1.30.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0.31
description London Data VLAN
encapsulation dot1Q 31
ip address 10.1.31.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0.32
description London Voice VLAN
encapsulation dot1Q 32
ip address 10.1.32.1 255.255.255.0
!
router ospf 1
router-id 3.3.3.3
log-adjacency-changes
network 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
network 10.1.30.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
network 10.1.31.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
network 10.1.32.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.3
!
ntp source FastEthernet0/0
ntp update-calendar
ntp server 10.1.1.4
6. As mentioned above, I am leveraging a NME-16ES-1G-P Ethernet Switch Module to function as a “3750” in London. For all intents and purposes, the router “views” this module as a separate device. See
here for a detailed explanation and
here for an example of how I previous configured this module. Below is the pertinent configuration.
london-s1#
!
clock timezone GMT 0
clock summer-time BST recurring
!
!
interface FastEthernet1/0/1
description london ip phones
switchport access vlan 31
switchport voice vlan 32
spanning-tree portfast
!
interface FastEthernet1/0/2
description london ip phones
switchport access vlan 31
switchport voice vlan 32
spanning-tree portfast
!
!etc…!
!
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
shutdown
!
interface Vlan30
description London Server Vlan
ip address 10.1.30.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan31
description London Data Vlan
ip address 10.1.31.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan32
description London Voice Vlan
ip address 10.1.32.2 255.255.255.0
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.30.1
!
7. Finally, some quick ping tests verify connectivity.
newyork#ping 172.16.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/28/32 ms
newyork#ping 172.16.1.6
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.1.6, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
newyork#ping 10.1.21.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.21.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/29/32 ms
newyork#ping 10.1.31.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.31.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/32/40 ms
newyork#